Nanobots Will Be Flowing Through Your Body By 2030

It was not until 1981 when microscopes capable of seeing individual atoms were produced. They gave a boost to the concept of nanotechnology. Since then, the field has seen massive advancements to the point that now experts claim that nanobots will be flowing through your body by 2030.
Some futurists believe that in the next 10 years or so, your blood will be infused with tiny nanorobots that will help you stay healthy and even transfer your thoughts to a wireless cloud. On a molecular level, they will move inside of you, preserving your biological system and guaranteeing that you live a healthy and long life. You are closer to the future than you may believe.
We have grown accustomed to little technologies and artificial intelligence in our daily lives, so the term “nano” is no longer considered unique. The potential applications of these minuscule devices have grown in tandem with technological advancements.
Ray Kurzweil, a futurist and Google director of engineering, is a frequent predictor of future events who professes to have a high accuracy record. He is one of the most outspoken proponents of the idea that nanobots will soon be circulating in our bloodstream. This prediction’s science may not be so far removed from present technology.
Nanobots injected into your bloodstream
DNA robots are already being studied in animals to find and destroy cancer cells, according to IFL Science. These DNA strands have the capacity to travel through the circulation, injecting blood clotting medicines into the blood vessels surrounding tumors, effectively cutting off their blood supply.
If human trials are successful, these tiny robots could revolutionize cancer treatment and cell research. However, there are still a lot of obstacles to overcome before injected nanorobots can outperform present treatment options.
Cancer diagnosis and treatment is one thing, but tiny nanobots could play a significant role in medicine in the future for other reasons. According to New Atlas, researchers predict nanobots will soon be able to administer medications to humans with high precision. This would enable microdoses to be delivered precisely where the patient needs them, potentially reducing undesirable side effects.
Nanobots, according to university scientists, could one day be employed to remove plaque in veins and alleviate dietary disorders, among a myriad of other medicinal applications. Nanobots have the potential to go beyond simple therapy and allow humans to achieve a higher level of connectivity.
Scientists from Harvard Medical School’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and Department of Genetics revealed in a study posted in ScienceMag:
“As a proof of principle, nanorobots loaded with combinations of antibody fragments were used in two different types of cell-signaling stimulation in tissue culture. Our prototype could inspire new designs with different selectivities and biologically active payloads for cell-targeting tasks.”
Nanobots might theoretically one day be employed to continuously monitor our bodies for diseases and other symptoms, sending this data to a cloud for close monitoring by medical personnel. This might effectively turn regular colds and other ailments into readily preventable diseases.
The notion that nanobots could one day broadcast our thoughts to the cloud is perhaps the most far-fetched of the numerous potential applications for nanobots. This feat would necessitate significant advances in neurology and nanorobotics, as well as a population prepared to grant Google direct access to our minds. While this capability may be possible in the future, it is most likely a long distance off.
Let us take a step back for a second and define what nanotechnology is.
What is nanotechnology?
Nanotechnology is a booming discipline that combines engineering and science, and it is not just for sci-fi villains.
Nanorobotics is the growing area of designing and building robots with components that are less than a nanometer in size ((109 meters), or spanning in size from 0.1 to 10 micrometers, and are composed of nanoscale or molecular components.
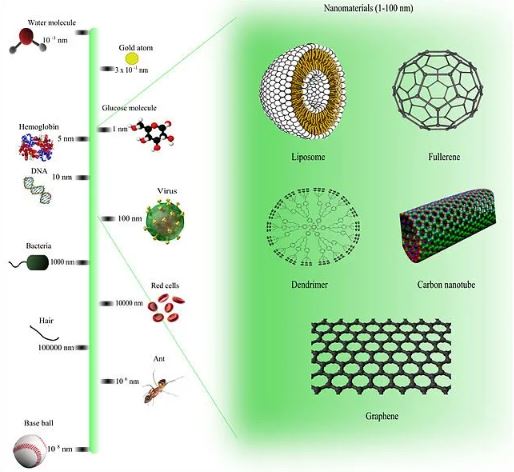
A nanotechnology scale that corresponded to other comprehensible items. Source: Wikimedia/Sureshbup
One nanometer is around ten times the size of a single atom and ten times smaller than the breadth of your DNA, for example.
Where nanotechnology began
Nanotechnology, on the other hand, has been around for quite some time. Some credit Nobel Laureate Richard Feynman with kicking off the discipline with a discussion titled “There’s Plenty of room at the Bottom” given to a group of physicists at the American Physical Society meeting at Caltech in 1959.
In his address, Feynman, who is known as the “Father of Nanotechnology,” presented a theoretical technique that would enable researchers to manage solitary atoms or molecules. This method, which had not yet been invented, would ultimately become the most important use of nanotechnology.
It was not until 1981 when microscopes capable of seeing individual atoms were produced. These early scanning tunneling microscopes attained previously unheard-of levels of precision and magnification. They gave a boost to the concept that nanotechnology was viable by allowing researchers to view individual atoms.
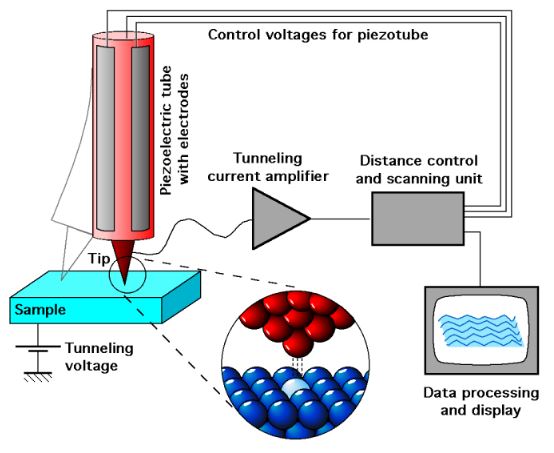
A diagram depicting the operation of a scanning tunneling microscope. Source: Michael Schmid
Nanotechnology and the future
Based on all of this, we face a slew of extremely serious hurdles ahead of us, and more research and development is required before we can begin using nanorobots.
According to some researchers, overcoming these obstacles and beginning to use nanobots for some types of surgery will take about ten years. Others, on the other hand, are skeptical that this is the wisest use of scarce health-care funds. Nanorobotics is anticipated to be similarly expensive – at least in the short to medium term – as robot-assisted surgery is presently more expensive than traditional procedures.
Kurzweil, for one, believes that nanotechnology holds the prospect of one day uniting humans and technology together. He told Engadget in 2019:
“The scenario that I have is that we will send medical nanorobots into our bloodstream. One application of these medical nanorobots will be to extend our immune systems. … These robots will also go into the brain and provide virtual and augmented reality from within the nervous system rather than from devices attached to the outside of our bodies. The most important application of the medical nanorobots is that we will connect the top layers of our neocortex to synthetic neocortex in the cloud.”
Would you volunteer to take the initial steps toward becoming a cyborg if nanobot injection becomes a viable option? Are you ready for a transition like this?
- Source : GreatGameIndia